
This will become clearer with the example below. It is necessary during the calculation of the APEs to go up to a maximum number of rows equal to the horizon. Compute the Absolute Percentage Errors (APEs) Thus, the training dataset contains the first 45 rows while the validation dataset contains last 15 rows. The goal is to get predictions of sales for the next twelve months. These events are the monthly sales of cars from January 2015 to December 2019. For this, I use an example of 60 events of historical data. Compute the Horizon-Wide Mean Absolute Percentage Error (HW-MAPE).MAPE (for a given horizon) = mean (APEs for a given horizon) Compute the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) for different horizons.Compute the Absolute Percentage Errors (APEs) by comparing predictive forecasts and actual.Three steps are necessary to compute the HW-MAPE: The refit process does not rebuild the predictive model, but adjust its parameters.įig 1: Validation dataset versus training dataset

Note that once the predictive model is selected, it is refitted on the whole period, including validation. The remaining 25% is used to validate the predictive model.The first 75% of the data is used to train the predictive model.The historical dataset is considered in the chronological order by the prediction engine and is split into two parts: Smart Predict uses the validation dataset to estimate the HW-MAPE. Now let’s see what the steps are to compute this indicator. It is from this internal table that all the steps of the calculation of the HW_MAPE are done. When Smart Predict is creating prediction models, it also creates an internal table containing the predictions for all the range of the horizon and for all actual values of the validation dataset. This is to avoid a bias (tendency for the predictive forecasts to be consistently higher or lower than the actual value), due to an arbitrary choice of cut between past and future. Multiply the measure of the performance on several points of validation.Capture the performance of the predictive model with multi-horizon.Table 2: Actuals and forecasts on all the range of the horizon The table 1 above becomes like table 2 below with our example of a horizon of twelve months. If the behavior of data will not change between the past and the future, we will have all the information to compute our quality indicator. To do that, we generate the same number of predictions requested by the user also for historical values. The goal is to optimally capture the performance of the model, and to give an estimate of the expected performance on new data. To remedy to this, the idea is to calculate an expected MAPE. Table 1: Actuals and forecasts at one level. The following table illustrates this situation. Consequently, it is not possible to get a real HW-MAPE. The problem is that for the predicted events in the future, real values are not still known, and the comparison is not possible. To do that, we need to compare the predictions with the real values.
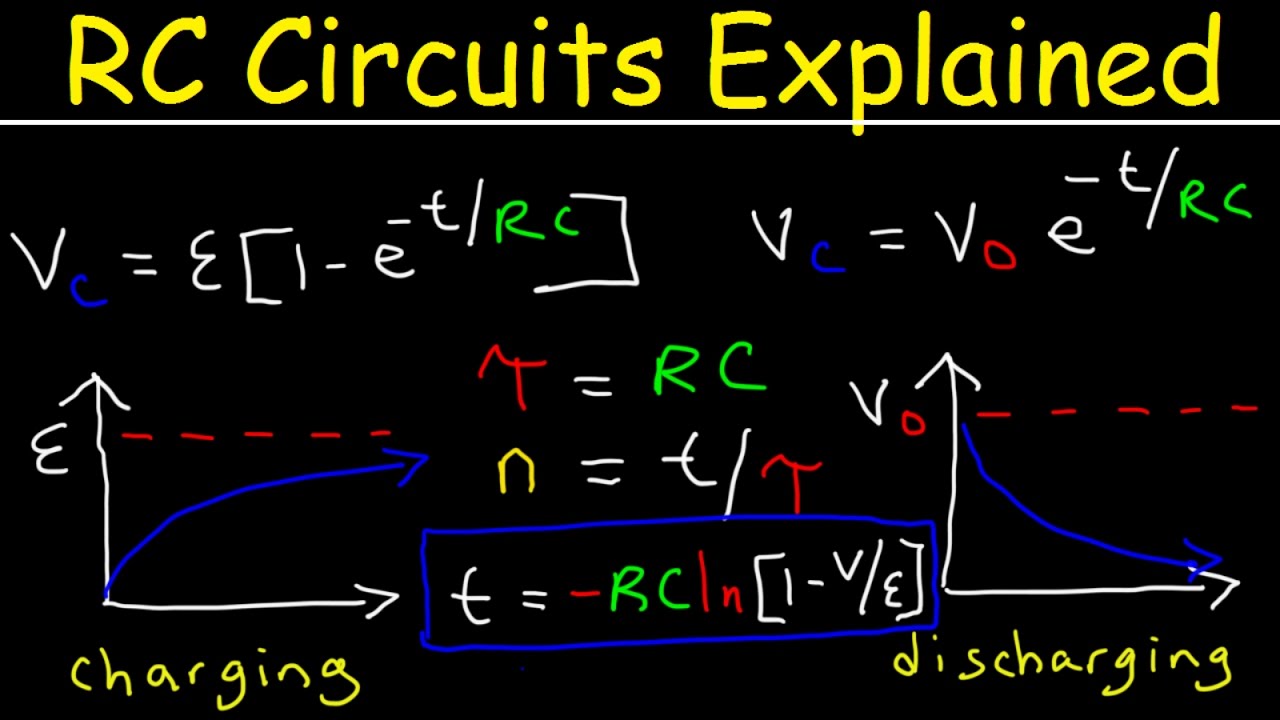
When the user requests forecasts, let’s say for the next twelve months, he needs an indicator that tells him how correct the predictive forecasts are. Thus, we can say that, the smaller the HW-MAPE is, the better the accuracy of the predictive forecasts. The smaller this distance is, the nearer the predictive forecasts will be from the actual values. In this average of average, a kind of distance is calculated. Again, it is an average of distances of all predictive forecasts from the actual values. It is a sum of terms divided by the number of these terms. The formula to calculate the MAPE is:Īgain, inspect this formula. It shows how much the forecast differs from the actual value. In fact, this formula is an average of a quality indicator calculated for the entire range of the horizon. What are the important parts of this formula? It is a sum of elements divided by the number of these elements. It refers to the period in the future you want to predict.

H is the horizon, or the number of forecasts requested by the user in the settings of the predictive scenario.Now, look at the definition of the HW-MAPE.
HW-MAPE with its horizon dimension (the number of forecasts requested in the future), fills this condition. This is the reason an indicator is needed that considers the number of predictive forecasts requested in the future. It is to have estimations for each month of the next year, or the daily evolution for the next month. When a user wants to estimate the revenue of his products, or how the stock will evolve, generally, it is not to have one prediction. The goal of this blog is to lift the veil on the following aspects of this indicator.
Series with time calc series#
When I wrote the blog Time Series Forecasting in SAP Analytics Cloud Smart Predict in Detail, I mentioned that the accuracy of predictive forecasts is calculated by an indicator named Horizon Wide Mean Absolute Percentage Error or in short the HW-MAPE.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
